PlanetScale
Add Prisma ORM to an existing TypeScript project with PlanetScale and learn database introspection and querying
PlanetScale is a serverless database platform. This guide covers both PlanetScale MySQL and PlanetScale Postgres. In this guide, you will learn how to add Prisma ORM to an existing TypeScript project, connect it to PlanetScale, introspect your existing database schema, and start querying with type-safe Prisma Client.
Prerequisites
1. Set up Prisma ORM
Navigate to your existing project directory and install the required dependencies:
MySQL
npm install prisma @types/node --save-dev
npm install @prisma/client @prisma/adapter-planetscale undici dotenvPostgres
npm install prisma @types/node @types/pg --save-dev
npm install @prisma/client @prisma/adapter-pg pg dotenv2. Initialize Prisma ORM
Set up your Prisma ORM project by creating your Prisma Schema file with the following command:
MySQL
npx prisma init --datasource-provider mysql --output ../generated/prismaPostgres
npx prisma init --datasource-provider postgresql --output ../generated/prismaThis command does a few things:
- Creates a
prisma/directory with aschema.prismafile containing your database connection configuration - Creates a
.envfile in the root directory for environment variables - Creates a
prisma.config.tsfile for Prisma configuration
The generated prisma.config.ts file looks like this:
import "dotenv/config";
import { defineConfig, env } from "prisma/config";
export default defineConfig({
schema: "prisma/schema.prisma",
migrations: {
path: "prisma/migrations",
},
datasource: {
url: env("DATABASE_URL"),
},
});The generated schema uses the ESM-first prisma-client generator with a custom output path:
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client"
output = "../generated/prisma"
}
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
relationMode = "prisma"
}PlanetScale MySQL requires relationMode = "prisma" because it doesn't support foreign key constraints.
3. Connect your database
Update the .env file with your PlanetScale connection URL:
DATABASE_URL="mysql://username:password@host.connect.psdb.cloud/mydb?sslaccept=strict"You can find your connection string in the PlanetScale dashboard.
PlanetScale Postgres connection types:
| Type | Port | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| Direct | 5432 | Prisma CLI commands (migrations, introspection), Prisma Studio |
| PgBouncer | 6432 | Application connections, serverless environments |
For production applications, we recommend using PgBouncer (port 6432) for application connections.
4. Introspect your database
Run the following command to introspect your existing database:
npx prisma db pullThis command reads the DATABASE_URL environment variable, connects to your database, and introspects the database schema. It then translates the database schema from SQL into a data model in your Prisma schema.
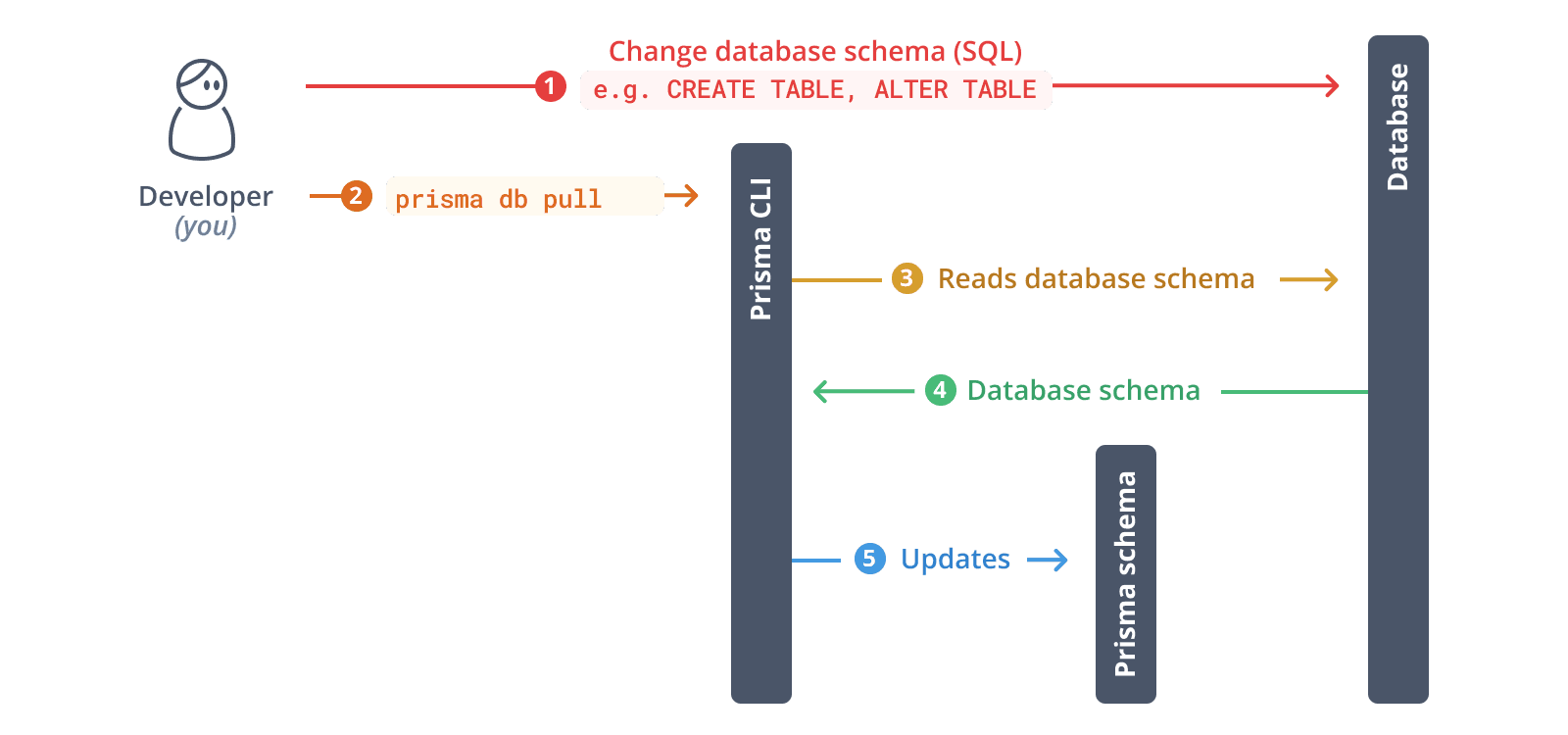
After introspection, your Prisma schema will contain models that represent your existing database tables.
5. Generate Prisma ORM types
Generate Prisma Client based on your introspected schema:
npx prisma generateThis creates a type-safe Prisma Client tailored to your database schema in the generated/prisma directory.
6. Instantiate Prisma Client
Create a utility file to instantiate Prisma Client. You need to pass an instance of the Prisma ORM driver adapter adapter to the PrismaClient constructor:
import "dotenv/config";
import { PrismaPlanetScale } from "@prisma/adapter-planetscale";
import { PrismaClient } from "../generated/prisma/client";
import { fetch as undiciFetch } from "undici";
const adapter = new PrismaPlanetScale({ url: process.env.DATABASE_URL, fetch: undiciFetch });
const prisma = new PrismaClient({ adapter });
export { prisma };7. Query your database
Now you can use Prisma Client to query your database. Create a script.ts file:
import { prisma } from "./lib/prisma";
async function main() {
// Example: Fetch all records from a table
// Replace 'user' with your actual model name
const allUsers = await prisma.user.findMany();
console.log("All users:", JSON.stringify(allUsers, null, 2));
}
main()
.then(async () => {
await prisma.$disconnect();
})
.catch(async (e) => {
console.error(e);
await prisma.$disconnect();
process.exit(1);
});Run the script:
npx tsx script.ts8. Evolve your schema
PlanetScale uses a branching workflow instead of traditional migrations. To make changes to your database schema:
8.1. Update your Prisma schema file
Update your Prisma schema file to reflect the changes you want to make to your database schema. For example, add a new model:
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
content String?
published Boolean @default(false)
authorId Int
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
posts Post[]
} 8.2. Push the changes to your development branch:
npx prisma db pushThis command will:
- Apply the schema changes to your PlanetScale database
- Regenerate Prisma Client
For production deployments, use PlanetScale's branching workflow to create deploy requests.
9. Explore your data with Prisma Studio
npx prisma studioNext steps
You've successfully set up Prisma ORM. Here's what you can explore next:
- Learn more about Prisma Client: Explore the Prisma Client API for advanced querying, filtering, and relations
- Database migrations: Learn about Prisma Migrate for evolving your database schema
- Performance optimization: Discover query optimization techniques
- Build a full application: Check out our framework guides to integrate Prisma ORM with Next.js, Express, and more
- Join the community: Connect with other developers on Discord