Multiple databases
Learn how to use multiple Prisma Clients in a single app to connect to multiple databases, handle migrations, and deploy your application to Vercel.
Introduction
This guide shows you how to use multiple databases using Prisma ORM in a single Next.js app. You will learn how to connect to two different Prisma Postgres databases, manage migrations, and deploy your application to Vercel. This approach is useful for multi-tenant applications or when you need to separate concerns when managing connections to multiple databases.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that you have the following:
- Node.js 20+ installed.
- A Prisma Data Platform account.
- A Vercel account (if you plan to deploy your application).
1. Set up a Next.js project
Create a new Next.js app using create-next-app from your desired directory:
npx create-next-app@latest my-multi-client-appYou will be prompted to answer a few questions about your project. Select all of the defaults.
For completeness, those are:
- TypeScript
- ESLint
- Tailwind CSS
- No
srcdirectory - App Router
- Turbopack
- Default custom import alias:
@/*
Then, navigate to the project directory:
cd my-multi-client-app2. Set up your databases and Prisma Clients
In this section, you will create two separate Prisma Postgres instances—one for user data and one for post data. You will also configure the Prisma schema and environment variables for each.
First, install Prisma and the required dependencies:
npm install prisma tsx @types/pg --save-devnpm install @prisma/client @prisma/adapter-pg dotenv pgIf you are using a different database provider (MySQL, SQL Server, SQLite), install the corresponding driver adapter package instead of @prisma/adapter-pg. For more information, see Database drivers.
You have installed the required dependencies for the project.
2.1. Create a Prisma Postgres instance to contain user data
Initialize Prisma with a Prisma Postgres instance by running:
npx prisma@latest init --dbIf you are not using a Prisma Postgres database, do not use the --db flag. Instead, create two PostgreSQL database instances and add their connection URLs to the .env file as PPG_USER_DATABASE_URL and PPG_POST_DATABASE_URL.
Follow the prompts to name your project and choose a database region.
The prisma@latest init --db command:
- Connects your CLI to your Prisma Data Platform account. If you are not logged in or do not have an account, your browser will open to guide you through creating a new account or signing into your existing one.
- Creates a
prismadirectory containing aschema.prismafile for your database models. - Creates a
.envfile with yourDATABASE_URL(e.g.,DATABASE_URL="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database?sslmode=require").
Rename the prisma folder to prisma-user-database:
mv prisma prisma-user-databaseEdit your .env file to rename DATABASE_URL to PPG_USER_DATABASE_URL:
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database?sslmode=require" // [!code --]
PPG_USER_DATABASE_URL="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database?sslmode=require" // [!code ++]Open prisma-user-database/schema.prisma file and update it to define a User model. Also, set the environment variable and specify a custom output directory for the generated Prisma Client:
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client"
output = "../prisma-user-database/user-database-client-types"
}
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
} Create a prisma.config.ts file for the user database:
import "dotenv/config";
import { defineConfig, env } from "prisma/config";
export default defineConfig({
schema: "prisma-user-database/schema.prisma",
migrations: {
path: "prisma-user-database/migrations",
},
datasource: {
url: env("PPG_USER_DATABASE_URL"),
},
}); You'll need to install the dotenv package if you haven't already:
npm install dotenvYour user database schema is now ready.
2.2. Create a Prisma Postgres instance for post data
Repeat the initialization for the post database:
npx prisma init --dbAfter following the prompts, rename the new prisma folder to prisma-post-database:
mv prisma prisma-post-databaseRename the DATABASE_URL variable in .env to PPG_POST_DATABASE_URL:
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database?sslmode=require" // [!code --]
PPG_POST_DATABASE_URL="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database?sslmode=require" // [!code ++]Edit the prisma-post-database/schema.prisma file to define a Post model. Also, update the datasource URL and set a custom output directory:
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client"
output = "../prisma-post-database/post-database-client-types"
}
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
content String?
} Create a prisma.config.ts file for the post database:
import "dotenv/config";
import { defineConfig, env } from "prisma/config";
export default defineConfig({
schema: "prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
migrations: {
path: "prisma-post-database/migrations",
},
datasource: {
url: env("PPG_POST_DATABASE_URL"),
},
}); Your post database schema is now set.
2.3. Add helper scripts and migrate the schemas
To simplify your workflow, add helper scripts to your package.json file that run Prisma commands for both databases:
"script":{
"dev": "next dev --turbopack",
"build": "next build",
"start": "next start",
"lint": "next lint",
"postinstall": "npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"generate": "npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"migrate": "npx prisma migrate dev --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma migrate dev --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"deploy": "npx prisma migrate deploy --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma migrate deploy --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"studio": "npx prisma studio --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma --port 5555 & npx prisma studio --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma --port 5556"
}Here is an explanation of the custom scripts:
postinstall: Runs immediately after installing dependencies to generate Prisma Clients for both the user and post databases using their respective schema files.generate: Manually triggers the generation of Prisma Clients for both schemas, ensuring your client code reflects the latest models.migrate: Applies pending migrations in development mode for both databases using Prisma Migrate, updating their schemas based on changes in your Prisma files.deploy: Executes migrations in a production environment, synchronizing your live databases with your Prisma schemas.studio: Opens Prisma Studio for both databases simultaneously on different ports (5555for the user database and5556for the post database) for visual data management.
Run the migrations:
npm run migrateWhen prompted, name the migration for each database accordingly.
3. Prepare the application to use multiple Prisma Clients
Next, create a lib folder to store helper files for instantiating and exporting your Prisma Clients:
mkdir -p lib && touch lib/user-prisma-client.ts lib/post-prisma-client.ts3.1. Instantiate and export the Prisma Client for the user database
In lib/user-prisma-client.ts, add the following code:
import { PrismaClient } from "../prisma-user-database/user-database-client-types/client";
import { PrismaPg } from "@prisma/adapter-pg";
const adapter = new PrismaPg({
connectionString: process.env.PPG_USER_DATABASE_URL,
});
const getPrisma = () =>
new PrismaClient({
adapter,
});
const globalForUserDBPrismaClient = global as unknown as {
userDBPrismaClient: ReturnType<typeof getPrisma>;
};
export const userDBPrismaClient = globalForUserDBPrismaClient.userDBPrismaClient || getPrisma();
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production")
globalForUserDBPrismaClient.userDBPrismaClient = userDBPrismaClient; 3.2. Instantiate and export the Prisma Client for the post database
In lib/post-prisma-client.ts, add this code:
import { PrismaClient } from "../prisma-post-database/post-database-client-types/client";
import { PrismaPg } from "@prisma/adapter-pg";
const adapter = new PrismaPg({
connectionString: process.env.PPG_POST_DATABASE_URL,
});
const getPrisma = () =>
new PrismaClient({
adapter,
});
const globalForPostDBPrismaClient = global as unknown as {
postDBPrismaClient: ReturnType<typeof getPrisma>;
};
export const postDBPrismaClient = globalForPostDBPrismaClient.postDBPrismaClient || getPrisma();
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production")
globalForPostDBPrismaClient.postDBPrismaClient = postDBPrismaClient; 4. Integrate multiple Prisma Clients in your Next.js app
Modify your application code to fetch data from both databases. Update the app/page.tsx file as follows:
import { postDBPrismaClient } from "@/lib/post-prisma-client";
import { userDBPrismaClient } from "@/lib/user-prisma-client";
export default async function Home() {
const user = await userDBPrismaClient.user.findFirst();
const post = await postDBPrismaClient.post.findFirst();
return (
<main className="min-h-screen bg-gray-50 py-12">
<div className="max-w-4xl mx-auto px-4">
<header className="mb-12 text-center">
<h1 className="text-5xl font-extrabold text-gray-900">Multi-DB Showcase</h1>
<p className="mt-4 text-xl text-gray-600">
Data fetched from two distinct databases.
</p>
</header>
<section className="mb-8 bg-white shadow-md rounded-lg p-6">
<h2 className="text-2xl font-semibold text-gray-800 border-b pb-2 mb-4">
User Data
</h2>
<pre className="whitespace-pre-wrap text-sm text-gray-700">
{user ? JSON.stringify(user, null, 2) : "No user data available."}
</pre>
</section>
<section className="bg-white shadow-md rounded-lg p-6">
<h2 className="text-2xl font-semibold text-gray-800 border-b pb-2 mb-4">
Post Data
</h2>
<pre className="whitespace-pre-wrap text-sm text-gray-700">
{post ? JSON.stringify(post, null, 2) : "No post data available."}
</pre>
</section>
</div>
</main>
);
} 4.1. Populate your databases with data
In a separate terminal window, open two instances of Prisma Studio to add data to your databases by running the script:
npm run studioThis will open up two browser windows, one in http://localhost:5555 and one in http://localhost:5556. Navigate to those windows and add sample data to both databases.
4.2. Run the development server
Before starting the development server, note that if you are using Next.js v15.2.0, do not use Turbopack as there is a known issue. Remove Turbopack from your dev script by updating your package.json:
"script":{
"dev": "next dev --turbopack",
"dev": "next dev",
"build": "next build",
"start": "next start",
"lint": "next lint",
"postinstall": "npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"generate": "npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma generate --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"migrate": "npx prisma migrate dev --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma migrate dev --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"deploy": "npx prisma migrate deploy --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma && npx prisma migrate deploy --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma",
"studio": "npx prisma studio --schema ./prisma-user-database/schema.prisma --port 5555 & npx prisma studio --schema ./prisma-post-database/schema.prisma --port 5556"
}In a separate terminal window, start the development server by running:
npm run devNavigate to http://localhost:3000 to see your Next.js app display data from both databases:
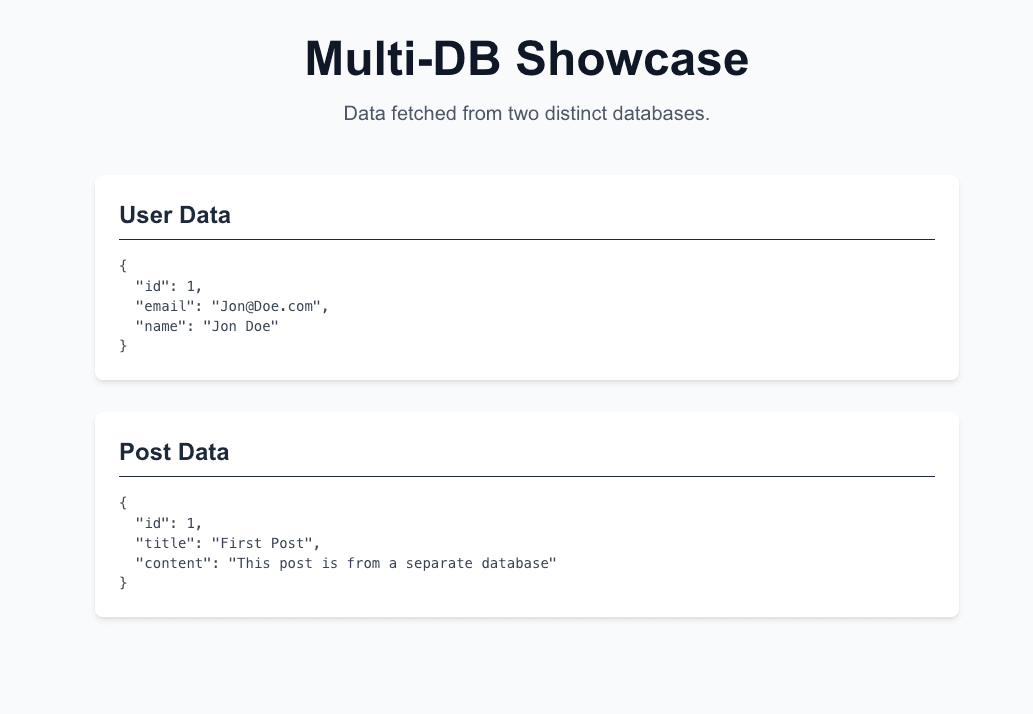
Congratulations, you have a Next.js app running with two Prisma Client instances querying different databases.
5. Deploy your Next.js app using multiple databases to Vercel
Deploy your app by following these steps:
- Ensure your project is version-controlled and pushed to a GitHub repository. If you do not have a repository yet, create one on GitHub. Once the repository is ready, run the following commands:
git add . git commit -m "Initial commit with Prisma Postgres integration" git branch -M main git remote add origin https://github.com/<your-username>/<repository-name>.git git push -u origin mainReplace
<your-username>and<repository-name>with your GitHub username and the name of your repository. - Log in to Vercel and navigate to your Dashboard.
- Create a new project. Follow Vercel's Import an existing project guide, but stop at step 3 where you will configure environment variables before clicking Deploy.
- Configure the
DATABASE_URLenvironment variable:- Expand the Environment variables section.
- Add the
PPG_USER_DATABASE_URLenvironment variable:- Key:
PPG_USER_DATABASE_URL - Value: Paste your user database connection URL, e.g. by copying it from the
.envfile in your project.
- Key:
- Add the
PPG_POST_DATABASE_URLenvironment variable:- Key:
PPG_POST_DATABASE_URL - Value: Paste your post database connection URL, e.g. by copying it from the
.envfile in your project.Do not deploy without setting the environment variables. Your deployment will fail if the application cannot connect to the databases.
- Key:
- Click the Deploy button. Vercel will build your project and deploy it to a live URL.
Open the live URL provided by Vercel and verify that your application is working.
Congratulations! You have deployed an application that uses multiple Prisma Clients to query two different databases, and it is now live and fully operational on Vercel.
Next steps
In this guide, you learned how to use multiple databases using Prisma ORM in a single Next.js app by:
- Setting up separate Prisma schemas for user and post databases.
- Configuring custom output directories and environment variables.
- Creating helper scripts to generate and migrate each schema.
- Instantiating and integrating multiple Prisma Clients into your application.
- Deploying your multi-database application to Vercel.
This approach allows you to maintain a clear separation of data models and simplifies multi-tenant or multi-database scenarios.
For further improvements in managing your project, consider using a monorepo setup. Check out our related guides: